|
|
|
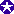 |
Boeing
B-1 Lancer |
|
The
B-1 is the backbone of America's long-range bomber force providing
massive and rapid delivery of precision and non-precision weapons
against any potential adversary anywhere around the globe on short
notice. It's blended wing/body configuration, along with
variable-geometry design and turbofan engines, combine to provide
greater range and high speed with enhanced survivability.
The ongoing Conventional Mission Upgrade
Program is significantly enhancing the B-1B's capability. This
gives the B-1B greater lethality and survivability through the
integration of precision and standoff weapons and a robust
electronic countermeasures suite. The upgrade program includes GPS
receivers a MIL-STD-1760 weapon interface enabling Joint Direct
Attack Munitions and other weapons, secure radios, and improved
computers to support new precision and near-precision weapons such
as the wind-corrected munitions dispenser, the joint standoff
Weapon, the joint air-to-surface standoff missile.
The B-1A model of the new
long-range multi-role bomber never went into production. USAF
acquired four prototype flight test models in the 1970s, but the
program was canceled in 1977. Flight test of the four B-1A models
continued through 1981. The B-1B is the improved variant initiated
by the Reagan administration in 1981. The first production model
flew in October 1984, and the first B-1B was delivered to Dyess
Air Force Base, Texas, in June 1985, with initial operational
capability on Oct. 1, 1986. The final B-1B was delivered May 2,
1988. The B-1B holds several world records for speed,
payload and distance. The National Aeronautic Association
recognized the B-1B for completing one of the 10 most memorable
record flights for 1994. The B-1B was first used in combat
in support of operations against Iraq during Operation Desert Fox
in December 1998. B-1s have been subsequently used in Operation
Allied Force. |
|
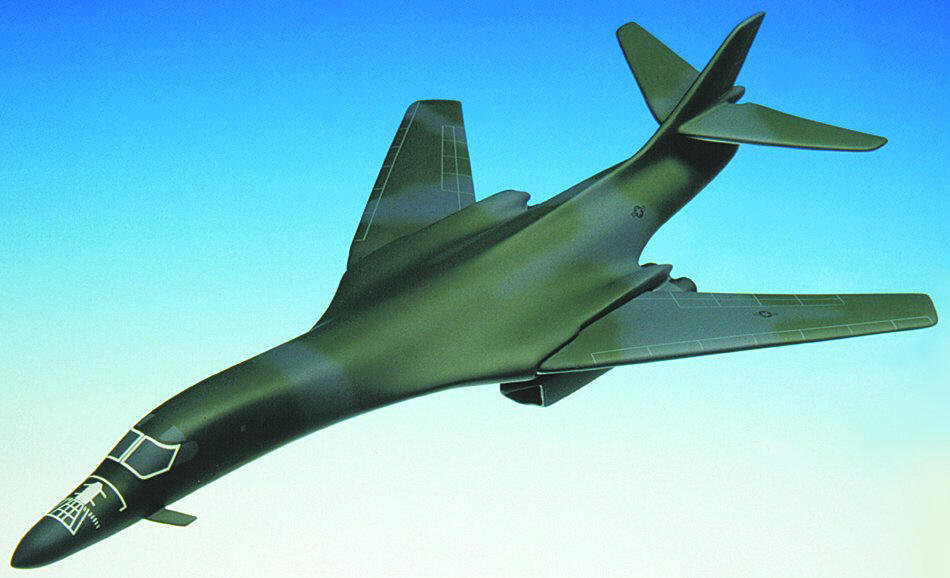 |
B-1B Lancer
Standard Series. Swing out wings. Wingspan 9" to 16"
x 17.5" long.
No. AGB1D-ST. Only $139.95 |
|
